Nutrition for Injury Recovery
Tuesday, March 5, 2024
Understandably, we want a fast recovery from injury to be able to return to our daily activities and get back onto our feet. In addition to our rehabilitation exercises and proper sleep, nutrition is a crucial factor that can contribute to enhancing your recovery.
Energy/Calories
The inclination to significantly reduce energy intake (create a calorie deficit) may arise with decreased physical activity; however, this is not advisable. Throughout the recovery phase, our body requires additional energy to ensure weight maintenance and preservation of lean muscle mass. A combination of ineffective training due to injury, and low energy intake can accelerate muscle loss. The goal is to adhere to maintenance calories to minimise both fat gain and muscle loss. Maintenance calories are the amount of energy or calories that your body requires to sustain its current weight while performing its normal functions (1).
Protein
Protein plays a crucial role in recovery to help reduce the risk of muscle and strength loss.
Current recommendations for adults during injury recovery is 1.6-2.5g of protein/kg/day (2).
Examples of protein:
- Lean beef, chicken, turkey, eggs, fish, prawns
- Dairy products: natural yoghurt, milk, hard cheese
- Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, tofu, edamame beans
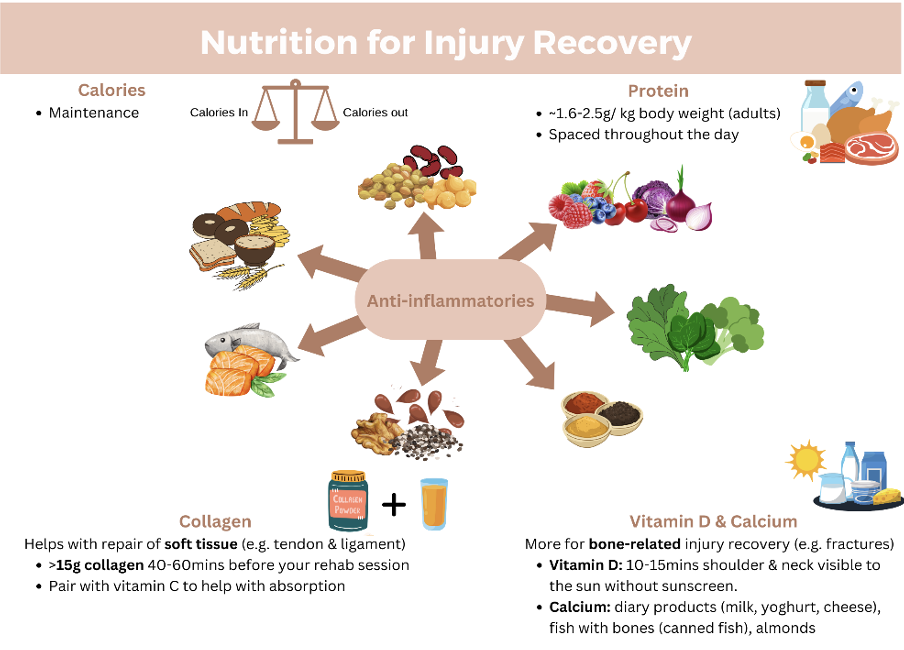
Anti-inflammatory Foods
Anti-inflammatory foods assist in reducing inflammation within the body, contributing to enhanced mobility at the site of injury.
Examples of anti-inflammatory foods:
Omega-3 (animal-based is more readily absorbed than plant-based).
- Animal: 2-3x oily fish per week: salmon, sardines, mackerel, or a fish oil tablet
- Plant: Chia seeds, walnuts, linseeds daily
Wholegrains & legumes (our main sources of fibre).
- Oats, wholegrain bread, spelt pasta, brown rice, quinoa
- Lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, black beans
Dark leafy greens (the darker in colour, the better)
- Kale, silverbeet, spinach, broccoli
Bright red, blue, purple fruit & vegetables
- Berries, cherries, acai, red grapes
- Beetroot, red cabbage, purple flesh potato
Spices (the stronger the flavour the more antioxidants it contains)
- Ginger, garlic, cinnamon, cloves, turmeric (pair with black pepper to activate the antioxidant properties)
Green Tea

Supplements
Meeting our increased nutritional needs solely through food can be challenging, which is where the value of supplements come into play.
Vitamin D and Calcium
Vitamin D and calcium are both crucial nutrients for our bone health, and particularly for any bone related injuries, such as fractures. If you are deficient in vitamin D, or if you do not consume many dairy products, taking a vitamin D and calcium supplement may be beneficial (1 & 2).
Collagen and Gelatine
For any soft tissue injuries (such as ligaments or tendons), emerging research suggests that collagen may help to enhance injury repair.
Choosing a collagen supplement over whey protein is based on the fact that collagen contains specific amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, which aid in the repair of soft tissue. In contrast, whey protein is primarily utilised for muscle building (3).
Protocol:
- >15g hydrolysed collagen, 40-60 minutes before your rehab exercises. This is when the collagen is at its peak in the blood stream.
- Pair collagen with sources of vitamin C to help with the absorption (e.g. orange juice, piece of fruit)
Creatine
Supplementing with creatine is mainly to help prevent any loss of muscle and strength. Again, more research needs to be conducted in this area, but it may be beneficial for those on a longer rehab recovery period (2 & 3).
Protocol:
- Loading phase: 20g per day for 5 days
- ~5g per day thereafter
Naturally, we desire a fast recovery from injury to resume our daily routines and regain mobility. Alongside rehabilitation exercises and adequate rest, nutrition plays a pivotal role in improving your recovery process. You can always speak to your Allied Health professional for some specific advice.
References:
1. Nutritional Considerations and Strategies to Facilitate Injury Recovery and Rehabilitation
This blog is written by
Lyndal Schnabel
Author, Accredited Practicing Dietician and Head Coach at Lyndal Schnabel Dietitian

![]() Written on behalf of Physio Inq Sutherland
Written on behalf of Physio Inq Sutherland
